 Philip Aston published the paper “Simulating the influence of plasma protein on measured receptor affinity in biochemical assays reveals the utility of Schild analysis for estimating compound affinity for plasma proteins” with co-authors Daniel Blakeley (Novartis), David Sykes (Nottingham), Penny Ensor (Nottingham), Enric Bertran (Roche Innovation Center), and Steven Charlton (Nottingham) in the British Journal of Pharmacology in November 2015. This paper has now been selected as one of 22 Editor’s Choice articles from all the articles published by the journal in 2015.
Philip Aston published the paper “Simulating the influence of plasma protein on measured receptor affinity in biochemical assays reveals the utility of Schild analysis for estimating compound affinity for plasma proteins” with co-authors Daniel Blakeley (Novartis), David Sykes (Nottingham), Penny Ensor (Nottingham), Enric Bertran (Roche Innovation Center), and Steven Charlton (Nottingham) in the British Journal of Pharmacology in November 2015. This paper has now been selected as one of 22 Editor’s Choice articles from all the articles published by the journal in 2015.
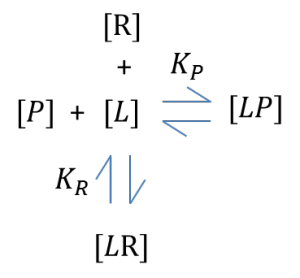
This work uses mathematical modelling to explore the potential utility of receptor binding and cellular functional assays for estimating the affinity of compounds for plasma proteins. Plasma proteins are routinely added to in vitro assays, so a secondary goal was to investigate the effect of plasma proteins on observed ligand-receptor interactions. The model demonstrates the profound influence of plasma protein binding on in vitro assays and identifies the utility of Schild analysis, which is usually applied to determine receptor-antagonist affinities, for calculating affinity at plasma proteins. Thus, these mathematical models can potentially be used in conjunction with experimental data to estimate drug-plasma protein affinities in the earliest phases of drug discovery programmes.
